The following sections will demonstrate how to create our sample application using some basic and some more advanced elements of DbForms.
For each form we are going to discuss here, we have included the JSP source code containing the DbForms elements followed by a representative screenshot of the resulting HTML page.
We suggest installing this tutorial application from the
examples/tutorial
directory in the distribution and taking a detailed look at it.
You will quickly find out how the elements behave and which
pattern of combined DbForms elements is best for each purpose.
Instructions for quickly installing the tutorial are described in
Section 7.5, “Installing the tutorial application”
.
For more detailed information about each DbForms custom element,
please refer to the DbForms Custom Tag Library document in the
docs/taglib directory. This
document contains a complete description of all DbForms tags and
their attributes.
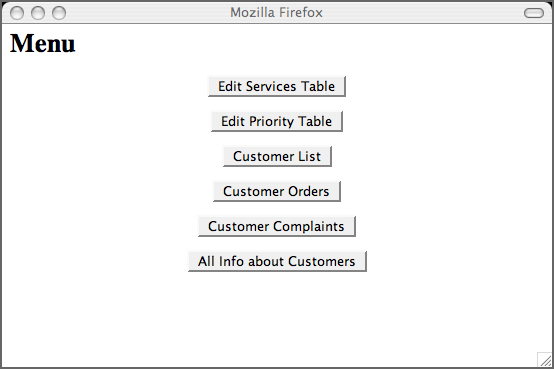
The main menu's only purpose is to link to the other pages. Of course, this could be done by simply coding html hyperlinks, but this section demonstrates how to use an empty element and how to use gotoButton elements.
Example 7.3. Code for menu.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="/WEB-INF/dbforms.tld" prefix="db" %>
<html>
<head>
<db:base/>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Menu</h1>
<db:dbform followUp="/menu.jsp">
<center>
<p>
<db:gotoButton caption="Edit Services Table"
destination="/services.jsp"/>
</p>
<p>
<db:gotoButton caption="Edit Priority Table"
destination="/priorities.jsp"/>
</p>
<p>
<db:gotoButton caption="Customer List"
destination="/customer_list.jsp"/>
</p>
<p>
<db:gotoButton caption="Browse Customer Orders"
destination="/customer_orders.jsp"/>
</p>
<p>
<db:gotoButton caption="Browse Customer Complaints"
destination="/customer_complaints.jsp"/>
</p>
<p>
<db:gotoButton caption="All Info about Customers"
destination="/customer_all.jsp"/>
</p>
</center>
</db:dbform>
</body>
</html>
Remarks
The
<%@taglib uri="/WEB-INF/dbForms.tld" prefix="db" %>
element refers to the Taglib Descriptor (tld) of DbForms
and defines the prefix used to identify the elements of
the tag library. (In our sample application we are using
db,
but you could use a different prefix.)
We used the following attributes of
db:gotoButton:
- caption: the caption of the button
- destination: the URL of the page to jump to
The
db:base
element should be included in every JSP that contains DbForms
elements. It ensures that images, Cascading Style Sheets and
relative links to other pages are found.
This page enables the user to administer an inventory of the services the company sells to its customers. The user will get a list of all the existing services along with text fields and buttons to update and delete rows. Finally an empty input form for inserting new services is also presented.
Example 7.4. Code for services.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="/WEB-INF/dbforms.tld" prefix="db" %>
<html>
<head>
<db:base/>
</head>
<body>
<db:errors/>
<db:dbform tableName="services" maxRows="*"
followUp="/services.jsp">
<db:header>
<db:gotoButton caption="Menu" destination="/menu.jsp" />
<h1>Services We Provide</h1>
<center>
<h3>Existing Service Definitions</h3>
</center>
<table border="5" width="60%" align="CENTER">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Description</th>
<th>Actions</th>
</tr>
</db:header>
<db:body>
<tr>
<td>
<db:textField fieldName="id" size="5"/>
</td>
<td>
<db:textField fieldName="name" size="20"
maxlength="30"/>
</td>
<td>
<db:textField fieldName="description" size="24"
maxlength="255"/>
</td>
<td>
<db:updateButton caption="Update"/>
<db:deleteButton caption="Delete"/>
</td>
</tr>
</db:body>
<db:footer>
</table>
<center><h3>Enter New Service Definition</h3></center>
<table align="center" border="3">
<tr>
<td>Id</td>
<td>
<db:textField size="5" fieldName="id"/>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Name</td>
<td>
<db:textField size="20" maxlength="30" fieldName="name"/>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Description</td>
<td>
<db:textArea rows="4" cols="20" wrap="virtual"
fieldName="description"/>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<br>
<center>
<db:insertButton caption="Store New Service Definition"
showAlways="true"/>
</center>
</db:footer>
</db:dbform>
</body>
</html>
Remarks
There is one HTML table for headings and rows of data. The
td
elements that define the column headings are in the
db:header
element because the header is rendered only once on the page. The
td
elements that define the rows of data are in the
db:body
element becase the row will be rendered many times if
multiple rows of data are retrieved from the database.
maxRows
is set to
*
which is equivalent to 'get all rows'. If the data
requested contains a great number of rows, we might
consider setting
maxRows
to 10, 20 or another limited number. If so, we would
instantiate navigation buttons for scrolling between the
pages. We will use that pattern later on.
The
db:errors
element shows a list of errors, if any occurred (i.e.
duplicate key error, etc.). The placement of this
element determines where the messages will be displayed.
The
db:updateButton
and
db:deleteButton
elements are placed in the body and are therefore rendered for each row.
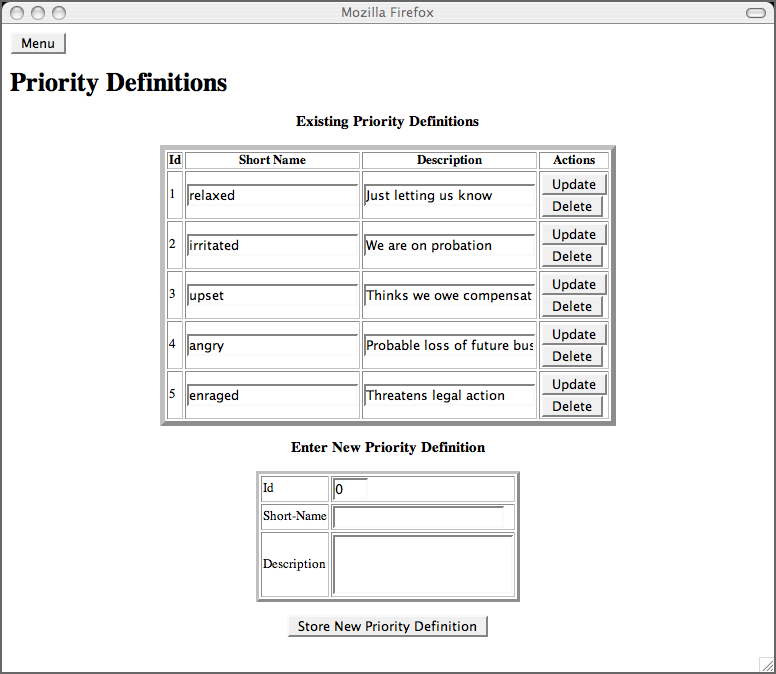
This page enables the user to manage a list of priorities we
will use this data later in the
complaints
page where we will prompt the user to select the appropriate
priority for a user's complaint.
Example 7.5. Code for priorities.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="/WEB-INF/dbforms.tld" prefix="db" %>
<html>
<head>
<db:base/>
</head>
<body>
<db:errors/>
<db:dbform tableName="priorities" maxRows="*"
followUp="/priorities.jsp" autoUpdate="true">
<db:header>
<db:gotoButton caption="Menu" destination="/menu.jsp" />
<h1>Priority Definitions</h1>
<center><h3>Existing Priority Definitions</h3></center>
<table border="5" width="60%" align="CENTER">
<tr>
<th>Id</th>
<th>Short Name</th>
<th>Description</th>
<th>Actions</th>
</tr>
</db:header>
<db:body>
<tr>
<td><db:label fieldName="id"/></td>
<td><db:textField fieldName="shortname"/></td>
<td><db:textField fieldName="description"/></td>
<td>
<db:updateButton caption="Update"/>
<db:deleteButton caption="Delete"/>
</td>
</tr>
</db:body>
<db:footer>
</table>
<center><h3>Enter New Priority Definition</h3></center>
<table border="3" align="center">
<tr>
<td>Id</td>
<td><db:textField size="3" fieldName="id"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Short-Name</td>
<td><db:textField fieldName="shortname"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Description</td>
<td><db:textArea rows="3" cols="20"
fieldName="description"/></td>
</tr>
</table>
<br>
<center>
<db:insertButton caption="Store New Priority Definition"
showAlways="true"/>
</center>
</db:footer>
</db:dbform>
</body>
</html>
Remarks
As you may have noticed, we have used a pattern for this page
that is similar to the pattern for
services.jsp.
The only real difference can be found in the
autoUpdate
attribute in the
db:form
element, which is set to
true
in
priorities.jsp.
This means, that all rows will be updated if their text fields
(and other data-sensitive elements such as pick lists)
have been edited by the
user. For example, if the user edits data in priorities numbered
1, 2 and 3 and then clicks a single update (or any other action
button),
all
changes will be stored
automatically
in the database! (These automatically triggered
events are called
implicit,
or
secondary
events.)x
This convenience page provides the user with a listing of all customers. The user is able to select a customer from the list and perform a given operation (edit orders, edit complaints submitted by the customer). The user will be able to delete existing customers, as well.
Example 7.6. Code for customer_list.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="/WEB-INF/dbforms.tld" prefix="db" %>
<html>
<head>
<db:base/>
</head>
<body>
<db:errors/>
<db:dbform tableName="customers" maxRows="*"
followUp="/customer_list.jsp"
autoUpdate="false">
<db:header>
<db:gotoButton caption="Menu" destination="/menu.jsp" />
<h1>Customer List</h1>
<table align="center" cellspacing="6">
<tr>
<td><b></b></td>
<td><b>First Name</b></td>
<td><b>Last Name</b></td>
<td><b>Address</b></td>
<td><b>P-Code</b></td>
<td><b>City</b></td>
<td><b>Action</b></td>
</tr>
</db:header>
<db:body allowNew="false">
<tr>
<td><db:associatedRadio name="r_customerkey" /></td>
<td><db:label fieldName="firstname"/></td>
<td><db:label fieldName="lastname"/></td>
<td><db:label fieldName="address"/></td>
<td><db:label fieldName="pcode"/></td>
<td><db:label fieldName="city"/></td>
<td><db:deleteButton caption="delete"/></td>
</tr>
</db:body>
<db:footer>
</table>
<p>
<center>
Show
<db:gotoButton caption="Orders"
destination="/customer_orders.jsp"
destTable="customers"
keyToKeyToDestPos="r_customerkey"/>
<db:gotoButton caption="Complaints"
destination="/customer_complaints.jsp"
destTable="customers"
keyToKeyToDestPos="r_customerkey"/>
<db:gotoButton caption="All Information"
destination="/customer_all.jsp"
destTable="customers"
keyToKeyToDestPos="r_customerkey"/>
of the selected customer!
</center>
</p>
</db:footer>
</db:dbform>
</body>
</html>
Remarks
In this page, we introduce a new pattern, the use of
db:associatedRadio
elements. To demonstrate the difference between this new
pattern and the old pattern, we have used
both
patterns in the customer list page. The delete buttons follow
the old pattern and the buttons for orders, complaints and all
information are implemented using the new pattern. Using
db:associatedRadio
elements to mark a row for certain actions (in
our case navigating to orders, complaints and all information)
saves a lot of space and makes for a cleaner interface. If we
had to include a button for all possible actions, the page would
not look very user-friendly.
You may have noticed that the
db:gotoButton
element has a strange sounding attribute
keyToKeyToDestPos.
The value of this attribute is generated by DbForms and links
the row in the page that is associated with the radio button
with the corresponding row in the Customers table. It refers to
the primary key in the Customers table and is used to identify
the row the system will jump to when the user clicks an action
button.
Another interesting item is that the attribute
allowNew
in the
db:body
element is set to a value of
false.
This has the effect, in the case of an empty result set (no
customers), of bypassing the body element altogether.
This page provides the user with the ability to manage new orders for a given customer. The user is able to edit customer orders, as well as customer data. The user should not be required to 'struggle' with item numbers, but instead, should be able to simply select (from a drop down select box) the services the customer has indicated they wish to purchase.
Example 7.7.
Code for
customer_orders.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="/WEB-INF/dbforms.tld" prefix="db" %>
<html>
<head>
<db:base/>
</head>
<body>
<!-- show any database errors here -->
<db:errors/>
<db:dbform tableName="customers" maxRows="1"
followUp="/customer_orders.jsp" autoUpdate="false">
<db:header>
<db:gotoButton caption="Menu" destination="/menu.jsp" />
<h1>Customer Orders</h1>
</db:header>
<db:body>
<table align="center">
<tr>
<td>Id</td>
<td>
<db:textField fieldName="id" size="4"/>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>First Name</td>
<td>
<db:textField fieldName="firstname" size="18"/>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Last Name</td>
<td>
<db:textField fieldName="lastname" size="18"/>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Address:</td>
<td>
<db:textField fieldName="address" size="25" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Postal Code - City</td>
<td>
<db:textField fieldName="pcode" size="6"/> -
<db:textField fieldName="city" size="16"/>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<br>
<!-- table embedding the sub form -->
<table align="center" border="1">
<tr>
<td>
<center><p><b>Orders</b></p></center>
<!-------- sub form begin ------->
<db:dbform tableName="orders" maxRows="2"
parentField="id" childField="customer_id"
followUp="/customer_orders.jsp"
autoUpdate="false">
<db:header>
<!-- Show existing orders of services for the customer -->
<table width="100%">
<tr>
<td width="40"></td>
<td>Service</td>
<td>Order Date</td>
</tr>
</db:header>
<db:body allowNew="true">
<tr>
<td width="40">
<db:associatedRadio name="radio_order"/>
</td>
<td>
<db:select fieldName="service_id">
<db:tableData
name = "our_services"
foreignTable = "services"
visibleFields = "name"
storeField = "id"
/>
</db:select>
</td>
<td>
<db:textField fieldName="orderdate" size="14"/>
</td>
</tr>
</db:body>
<db:footer>
<tr>
<td colspan="3" align="CENTER">
<db:updateButton caption="Update Order"
associatedRadio="radio_order"/>
<db:deleteButton caption="Delete Order"
associatedRadio="radio_order"/>
<db:insertButton caption="Store New Order"
showAlways="false" />
<db:navNewButton caption="New Order"
showAlwaysInFooter="false" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<br>
<center>
<db:navFirstButton caption="<< First" />
<db:navPrevButton caption="< Previous" />
<db:navNextButton caption="Next >" />
<db:navLastButton caption="Last >>" />
</center>
</db:footer>
</db:dbform>
<!-------- sub form end -------->
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<!-- end of table embedding the sub form -->
<br>
<center>
<db:insertButton caption="Store New Customer" />
<db:updateButton caption="Update Customer" />
<db:deleteButton caption="Delete Customer" />
<db:navNewButton caption="New Customer"
showAlwaysInFooter="false" />
</center>
</db:body>
<db:footer>
<br>
<center>
<db:navFirstButton caption="<< First" />
<db:navPrevButton caption="< Previous" />
<db:navNextButton caption="Next >" />
<db:navLastButton caption="Last >>" />
</center>
</db:footer>
</db:dbform>
</body>
</html>
Remarks
In this page, we have introduced several new DbForm features.
Nested Forms: The structure of this page is similar
to the structure shown in
Section 2.2.2.1, “The structure of a DbForms View”
where a main form has a subform in its body. The subform
is linked to its parent by the equality of one or more
data fields defined in the child form's
parentField
and
childField
attributes. If there is more than one field to define for
correct mapping, a field list may be provided, with each field
separated from the other by commas or semicolons.
Select Element: In addition to
db:textField:
and
db:textArea
elements, more complex elements like
db:select,
db:radio and
db:checkbox
can be used for data visualization and manipulation. The
db:select
element to allows the user to choose the type of services
available from a pulldown list.
External data fetched by a
db:tableData
element: This element provides external data for
db:radio,
db:checkbox or
db:select
elements. It may be used for cross references to other
tables. In our case, we initialized the select box with external
data from the service table. Be aware that you have to
distinguish between the field(s) to be
shown
to the user and the field to be
stored
in the associated field in the table. In our case we
showed
the field
service.name
and
stored
the value
service.id
in the associated field
orders.service_id!
The name
our_services
was defined to enable internal caching of the data,
which increases performance.
Navigation Buttons: Because only
one
customer is visible at once, the user needs a means of
navigating between records. This functionality is provided by the
db:navFirstButton,
db:navLastButton,
db:navPrevButton,
and
db:navNextButton
elements. In addition, using the second set of navigation
buttons, the user can navigate through a list of orders if there
are more than the maxRows that are displayed in the subform.
The
db:navNewButton
element navigates the user to an empty form. This form is
automatically created by DbForms. It is the same as this page,
but the fields are not populated and the insert button that we
defined in this JSP is present but the update and delete buttons
are not present.
This page is conceptually similar to the previous JSP
(customer_orders.jsp).
It provides the user with the ability to manage customer
complaints. The user is, once again, able to edit customer
complaints as well as customer data, all from the same page.
To establish an order of importance, every reported complaint must be associated with a priority level. To make life easier for our users, they are able to simply pick a priority level from a maintainable list of predefined priority levels.
Example 7.8.
Code for
customer_complaints.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="/WEB-INF/dbforms.tld" prefix="db" %>
<html>
<head>
<db:base/>
</head>
<body>
<!-- show any database errors here -->
<db:errors/>
<db:dbform tableName="customers" maxRows="1"
followUp="/customer_complaints.jsp" autoUpdate="false">
<db:header>
<db:gotoButton caption="Menu" destination="/menu.jsp" />
<h1>Customer Complaints</h1>
</db:header>
<db:body>
<table align="center">
<tr>
<td>Id</td>
<td>
<db:textField fieldName="id" size="4"/>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>First Name</td>
<td><db:textField fieldName="firstname" size="18"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Last Name</td>
<td><db:textField fieldName="lastname" size="18"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Address:</td>
<td><db:textField fieldName="address" size="25" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Postal Code - City</td>
<td>
<db:textField fieldName="pcode" size="6"/> -
<db:textField fieldName="city" size="16"/>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<br>
<!-- table embedding the sub form -->
<table align="center" border="1">
<tr>
<td>
<center><p><b>Complaints</b></p></center>
<!-------- sub form begin ------->
<db:dbform tableName="complaints" maxRows="2"
parentField="id" childField="customer_id"
followUp="/customer_complaints.jsp"
autoUpdate="false">
<db:header>
<!-- Show existing complaints of the customer -->
<table>
<tr>
<td width="40"></td>
<td valign="top">User's Message</td>
<td>Priority<br/><db:sort fieldName="priority"/></td>
<td>Incoming Date<br/><db:sort
fieldName="incomingdate"/></td>
</tr>
</db:header>
<db:body allowNew="true">
<tr>
<td width="40" valign="top">
<db:associatedRadio name="radio_complaint" />
</td>
<td valign="top">
<db:textArea fieldName="usermessage"
cols="32" rows="3" wrap="virtual"/>
</td>
<td valign="top">
<db:select fieldName="priority">
<db:tableData
name = "some_priorities"
foreignTable = "priorities"
visibleFields = "shortname"
storeField = "id"
/>
</db:select>
</td>
<td valign="top">
<db:textField fieldName="incomingdate" size="14"/>
</td>
</tr>
</db:body>
<db:footer>
<tr>
<td colspan="4" align="CENTER">
<db:updateButton caption="Update Complaint"
associatedRadio="radio_complaint"/>
<db:deleteButton caption="Delete Complaint"
associatedRadio="radio_complaint "/>
<db:insertButton caption="Store New Complaint"
showAlways="false" />
<db:navNewButton caption="New Complaint"
showAlwaysInFooter="false" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<br/>
<center>
<db:navFirstButton caption="<< First" />
<db:navPrevButton caption="< Previous" />
<db:navNextButton caption="Next >" />
<db:navLastButton caption="Last >>" />
</center>
</db:footer>
</db:dbform>
<!-------- sub form end -------->
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<!-- end of table embedding the sub form -->
<br>
<center>
<db:insertButton caption="Store New Customer" />
<db:updateButton caption="Update Customer" />
<db:deleteButton caption="Delete Customer" />
<db:navNewButton caption="New Customer"
showAlwaysInFooter="false"/>
</center>
</db:body>
<db:footer>
<br>
<center>
<db:navFirstButton caption="<< First" />
<db:navPrevButton caption="< Previous" />
<db:navNextButton caption="Next >" />
<db:navLastButton caption="Last >>" />
</center>
</db:footer>
</db:dbform>
</body>
</html>
Remarks
In this page, the user can sort the complaints by either
priority or by date. The sort control boxes are placed under
the column headings using the
db:sort
element. To use this feature on a field, the field must be defined
as
isKey
or
sortable
in the
dbforms-config.xml file.
The
usermessage
field is very long, 255 characters. The
db:textArea
element is used to display this field. In our example, up to 96
characters is displayed on three lines.
This page was created by merging
customer_orders.jsp
and
customer_complaints.jsp
into one file and then removing the update capabilities
(radio buttons and update, etc. buttons).
A new technique was used in this form. Only excerpts of
the code are shown in the examples below. The complete JSP
source code is available in the tutorial application in the
examples/tutorial
directory of the distribution.
Example 7.9.
Defining a query with data from more than one table in
dbforms-config.xml
<query name="orders_and_servicenames"
from="orders,services"
where="orders.service_id=services.id"
orderBy="orderdate">
<field name="customer_id" fieldType="int"/>
<field name="name" fieldType="char"/>
<field name="orderdate" fieldType="char"/>
</query>
Example 7.10.
Displaying data from more than one table in a single form
(customers_all.jsp)
<!-------- first sub form begin ------->
<db:dbform tableName="orders_and_servicenames"
maxRows="2" parentField="id"
childField="customer_id"
followUp="/customer_all.jsp">
<db:header>
<!-- Show existing orders of services for the customer -->
<table width="100%">
<tr>
<td>Service</td>
<td>Order Date</td>
</tr>
</db:header>
<db:body allowNew="false">
<tr>
<td>
<db:textField fieldName="name"/>
</td>
<td>
<db:textField fieldName="orderdate" size="14"/>
</td>
</tr>
</db:body>
<db:footer>
</table>
Remarks
In a previous example, we used the
db:select
element along with a
db:radioButton
element to get the names for the types of services from the
Services table and display them in a pulldown list. This
displays the name of the current value of the service
id
and allows the user to change the value. But in
customers_all.jsp
we only want to display data rather than provide a capability
to update it. We cannot use the
db:select
and
db:radioButton
elements. We need to use a different technique to get and
display the names of the types of services.
This technique requires an addition in the
dbforms-config.xml
file. The
query
element called
orders_and_servicename.
contains an SQL query that joins the Orders and Services tables.
We get the data from the Orders table and the service names from
the Services table. Then, in the JSP, we use
query
in the same way that we have been using
table.
We reference this query in the
db:dbform
element and the field
name
in the
db:textField
element.